Carbon Credits Characteristics

Carbon Credits for a Greener and Sustainable Future
Carbon Credits are tradable units that represent the reduction, removal, or avoidance of one metric ton of carbon dioxide equivalent (tCO₂e) emissions.
In the agricultural sector, these credits offer farmers a powerful opportunity: to generate income by adopting climate-smart practices that also improve soil health, crop resilience, and long-term farm sustainability.
In practice, carbon credits are created through projects that actively reduce emissions or capture carbon from the atmosphere. For farmers, this might include:
- Adopting regenerative practices like cover cropping, no-till or low-till farming
- Enhancing soil organic carbon through composting or biochar
- Implementing agroforestry systems that integrate trees into cropland
- Managing livestock emissions more efficiently through improved feed or waste systems
Are you a farmer ready to earn from climate-smart agriculture?
rupiya.app makes it simple to generate, verify, and sell carbon credits.
Join our platform and get rewarded for protecting the planet—one farm at a time
Key Characteristics of Carbon Credits
1.Tangible Representation of Carbon Reduction
Each carbon credit represents one metric ton of CO₂ (or equivalent greenhouse gases) reduced or removed from the atmosphere.
- This means that for every carbon credit, there is a quantifiable reduction or removal of one metric ton of CO₂ or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases.
Carbon credits quantify environmental benefits in measurable units.
- By assigning a specific value (one metric ton of CO₂) to each credit, carbon credits provide a standardized and measurable way to account for and trade reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Tradability in Carbon Markets
Carbon credits act like financial assets. They can be bought, sold, or traded, just like stocks or commodities.
They are used in two main types of carbon markets:
- Regulated markets – Operate under government policies and emission caps.
- Voluntary markets – Allow companies to offset emissions beyond legal requirements.
Farmers can generate carbon credits by adopting sustainable practices such as:
- No-till or low-till farming
- Cover cropping or agroforestry
- Improved livestock and manure management
Once verified, these credits can be sold to:
- Corporations aiming to meet climate goals
- Organizations looking to balance their carbon footprints
3. Origin from Verified Emission Reduction Activities
- Only verified sustainable farming practices can generate valid carbon credits.
- Certification agencies ensure accuracy and prevent false claims.
- Verification adds credibility and ensures environmental integrity.
4. Additionality: Going Beyond Business-as-Usual
Credits must be “additional”—they should result from actions that go beyond regular farming practices.
Projects must deliver new emission reductions that wouldn’t have happened without the carbon credit incentive.
Farmers need to adopt new sustainable methods, such as:
- Agroforestry
- Residue-free farming
- Soil carbon sequestration
This ensures that carbon credits fund real climate impact, not just reward existing practices
5. Permanence: Long-Term Environmental Benefits
Carbon sequestration must last over time to ensure lasting climate impact.
Example: Soil carbon storage requires ongoing regenerative farming to keep carbon locked in the soil.
There’s a risk of reversal, such as carbon being released due to land use change or poor management.
Risk management tools like buffer pools are used to insure against such losses and maintain credit integrity.
6. Measurability and Verification
Carbon credits follow strict MRV protocols—Measurement, Reporting, and Verification. Farmers must provide scientific evidence of actual carbon reduction or sequestration.
Verification tools include:
- Satellite imagery
- Soil sampling
- Remote sensing technologies
These methods ensure transparency, accuracy, and trust in the carbon credit system.
7. Dual Impact: Environmental & Economic
- Carbon credits cut emissions through sustainable farming practices.
- Farmers earn extra income by selling verified credits.
- Sustainable methods become profitable, encouraging adoption.
- Farming continues uninterrupted, ensuring food production stays stable.
- Supports both climate goals and rural livelihoods.
8. Time-Bound Validity
- Carbon credits come with an expiry period—they must be used or sold within a set timeframe.
- Understanding the credit lifecycle is crucial for farmers and businesses to plan trading and avoid loss of value.
- Expired credits may lose value or become ineligible for offsetting emissions.
9. Influence of Market Demand & Pricing
- Carbon credit prices fluctuate based on supply and demand in global and local carbon markets.
- Key influencing factors include:
- Government climate policies
- Corporate net-zero and ESG commitments
- International carbon pricing trends
- Farmers’ earnings can rise or fall depending on these market dynamics.
10. Role in Achieving Net-Zero Goals
- Carbon credits help offset unavoidable emissions, enabling industries and countries to meet net-zero targets.
- They support India’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by promoting clean practices and climate-smart agriculture.
- Also drive rural economic growth by opening new revenue opportunities for farmers through green practices.
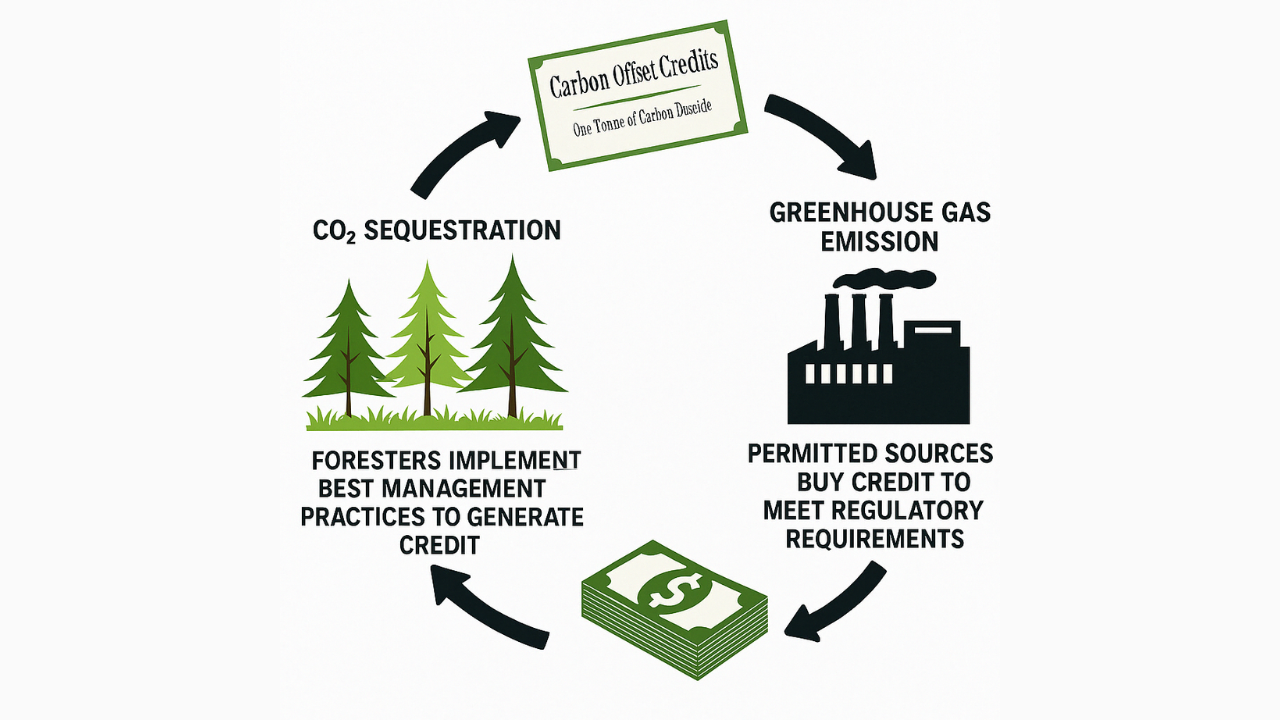
How understanding Carbon credit characteristics helps leverage carbon credits effectively
Understanding the key characteristics of carbon credits—like additionality, permanence, and verification—is essential for making them truly effective in fighting climate change. These factors ensure that credits represent real, lasting emission reductions and aren’t just greenwashing tools.
By also considering transparency, co-benefits, market dynamics and choosing high-quality credits, farmers, businesses, and policymakers can drive meaningful climate action while supporting economic growth.
Turn your farm into a climate hero. With rupiya.app, farmers can earn real income by adopting sustainable practices that generate verified carbon credits.
- Get access to carbon markets
- Support climate-smart agriculture
- Boosts soil health and productivity
- No complex paperwork—we handle it all
Join rupiya.app today and make every acre count—for your wallet and the planet.
FAQs
- What are carbon credits in agriculture?
Carbon credits in agriculture represent verified reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through climate-smart farming practices like no-till farming, cover cropping, and agroforestry.
- How can farmers earn money from carbon credits?
Farmers can adopt sustainable methods and generate carbon credits, which are then sold to companies seeking to offset their carbon footprint.
- What makes a carbon credit high-quality?
High-quality credits are additional, permanent, verifiable and come from projects that avoid social or environmental harm.
- Are carbon credits regulated?
Yes, carbon credits operate in both regulated and voluntary markets, often verified by global standards like Verra or Gold Standard.
- How does rupiya.app help with carbon credits?
Rupiya.app connects farmers to carbon markets, simplifies the verification process, and helps them earn revenue from sustainable farming practices.